USA Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
Sections for Health and Human Services (HHS)
- USA Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
- USA Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Secretary Kathleen Sebelius.
- USA Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Secretary’s Priorities.
USA Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
> USA Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). About HHS.

The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is the United States government’s principal agency for protecting the health of all Americans and providing essential human services, especially for those who are least able to help themselves.
HHS represents almost a quarter of all federal outlays, and it administers more grant dollars than all other federal agencies combined. HHS’ Medicare program is the nation’s largest health insurer, handling more than 1 billion claims per year. Medicare and Medicaid together provide health care insurance for one in four Americans.
HHS works closely with state and local governments, and many HHS-funded services are provided at the local level by state or county agencies, or through private sector grantees. The Department’s programs are administered by 11 operating divisions, including eight agencies in the U.S. Public Health Service and three human services agencies. The department includes more than 300 programs, covering a wide spectrum of activities. In addition to the services they deliver, the HHS programs provide for equitable treatment of beneficiaries nationwide, and they enable the collection of national health and other data.
Departmental leadership is provided by the Office of the Secretary. Also included in the Department is the Office of Public Health and Science, the Office of the HHS Inspector General and the HHS Office for Civil Rights. In addition, the Program Support Center, a self-supporting division of the Department, provides administrative services for HHS and other federal agencies.

> USA Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Historical Highlights
The roots of the Department of Health and Human Services go back to the earliest days of the nation:
1798
Passage of an act for the relief of sick and disabled seamen, which established a federal network of hospitals for the care of merchant seamen, forerunner of today’s U.S. Public Health Service.
1862
President Lincoln appointed a chemist, Charles M. Wetherill, to serve in the new Department of Agriculture. This was the beginning of the Bureau of Chemistry, forerunner to the Food and Drug Administration.
1871
Appointment of the first Supervising Surgeon (later called Surgeon General) for the Marine Hospital Service, which had been organized the prior year.
1878
Passage of the National Quarantine Act began the transfer of quarantine functions from the states to the federal Marine Hospital Service.
1887
The federal government opened a one-room laboratory on Staten Island for research on disease, thereby planting the seed that was to grow into the National Institutes of Health.
1891
Passage of immigration legislation, assigning to the Marine Hospital Service the responsibility for medical examination of arriving immigrants.
1902
Conversion of Marine Hospital Service into the Public Health and Marine Hospital Service in recognition of its expanding activities in the field of public health. In 1912, the name was shortened to the Public Health Service.
1906
Congress passed the Pure Food and Drugs Act, authorizing the government to monitor the purity of foods and the safety of medicines, now a responsibility of the FDA.
1912
President Theodore Roosevelt’s first White House Conference urged creation of the Children’s Bureau to combat exploitation of children.
1921
The Bureau of Indian Affairs Health Division was created, the forerunner to the Indian Health Service.
1930
Creation of the National Institute (late Institutes) of Health, out of the Public Health Service’s Hygienic Laboratory.
1935
Passage of the Social Security Act.
1938
Passage of the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act.
1939
The Federal Security Agency was created, bringing together related federal activities in the fields of health, education and social insurance.
1946
The Communicable Disease Center was established, forerunner of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The Cabinet-level Department of Health, Education and Welfare was created under President Eisenhower, officially coming into existence April 11, 1953. In 1979, the Department of Education Organization Act was signed into law, providing for a separate Department of Education. HEW became the Department of Health and Human Services, officially arriving on May 4, 1980. Some highlight dates in HEW and HHS history:
1955
Licensing of the Salk polio vaccine.
The Indian Health Service was transferred to HHS from the Department of Interior.
1961
First White House Conference on Aging.
1962
Passage of the Migrant Health Act, providing support for clinics serving agricultural workers.
1964
Release of the first Surgeon General’s Report on Smoking and Health.
1965
Creation of the Medicare and Medicaid programs, making comprehensive health care available to millions of Americans.
Also in 1965, the Older Americans Act created the nutritional and social programs administered by HHS’ Administration on Aging.
In addition, the Head Start program was created.
1966
International Smallpox Eradication program established — led by the U.S. Public Health Service, the worldwide eradication of smallpox was accomplished in 1977.
Also in 1966, the Community Health Center and Migrant Health Center programs were launched.
1970
Creation of the National Health Service Corps.
1971
National Cancer Act signed into law.
1975
Child Support Enforcement program established.
1977
Creation of the Health Care Financing Administration to manage Medicare and Medicaid separately from the Social Security Administration.
1980
Federal funding provided to states for foster care and adoption assistance.
1981
Identification of AIDS. In 1984, the HIV virus was identified by PHS and French scientists. In 1985, a blood test to detect HIV was licensed.
1984
National Organ Transplantation Act signed into law.
1988
Creation of the JOBS program and federal support for child care.
Passage of the McKinney Act to provide health care to the homeless.
1989
Creation of the Agency for Health Care Policy and Research (now the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality).
1990
Human Genome Project established.
Passage of the Nutrition Labeling and Education Act, authorizing the food label.
Also, the Ryan White Comprehensive AIDS Resource Emergency (CARE) Act began providing support for people with AIDS.
1993
The Vaccines for Children Program is established, providing free immunizations to all children in low-income families.
1995
The Social Security Administration became an independent agency.
1996
Enactment of welfare reform under the Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act.
Enactment of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
1997
Creation of the State Children’s Health Insurance Program (SCHIP), enabling states to extend health coverage to more uninsured children.
1999
The Ticket to Work and Work Incentives Improvement Act of 1999 is signed, making it possible for millions of Americans with disabilities to join the workforce without fear of losing their Medicaid and Medicare coverage. It also modernizes the employment services system for people with disabilities.
Initiative on combating bioterrorism is launched.
2000
Publication of human genome sequencing.
2001
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid is created, replacing the Health Care Financing Administration.
HHS responds to the nation’s first bioterrorism attack — delivery of anthrax through the mail.
2002
Office of Public Health Emergency Preparedness created to coordinate efforts against bioterrorism and other emergency health threats.
2003
Enactment of the Medicare Prescription Drug Improvement, and Modernization Act of 2003, the most significant expansion of Medicare since its enactment, including a prescription drug benefit.

> USA Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Secretaries of HEW and HHS
April 11, 1953 – July 31, 1955 – Oveta Culp Hobby
August 1, 1955 – July 31, 1958 – Marion B. Folsom
August 1, 1958 – January 19, 1961 – Arthur S. Flemming
January 21, 1961 – July 13, 1962 – Abraham Ribicoff
July 31, 1962 – August 17, 1965 – Anthony J. Celebrezze
August 18, 1965 – March 1, 1968 – John W. Gardner
May 16, 1968 – January 20, 1969 – Wilbur J. Cohen
January 21, 1969 – June 23, 1970 – Robert H. Finch
June 24, 1970 – January 29, 1973 – Elliot L. Richardson
February 12, 1973 – August 8, 1975 – Caspar W. Weinberger
August 8, 1975 – January 20, 1977 – David Mathews
January 25, 1977 – August 3, 1979 – Joseph A. Califano, Jr.
August 3, 1979 – January 20, 1981 – Patricia Roberts Harris
January 22, 1981 – February 3, 1983 – Richard S. Schweiker
March 9, 1983 – December 13, 1985 – Margaret M. Heckler
December 13, 1985 – January 20, 1989 – Otis R. Bowen, M.D.
March 1, 1989 – January 20, 1993 – Louis W. Sullivan, M.D
January 22, 1993 – January 20, 2001 – Donna E. Shalala
February 2, 2001 – January 26, 2005 – Tommy G. Thompson
January 26, 2005 – January 20, 2009 – Michael O. Leavitt
April 28, 2009 ………………………… – Kathleen Sebelius

> USA Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Operating & Staff Divisions
USA Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Operating Divisions.
The Department of Health and Human Services is the principal agency for protecting the health of all Americans. It is comprised of the Office of the Secretary and 11 operating divisions. The agencies perform a wide variety of tasks and services, including research, public health, food and drug safety, grants and other funding, health insurance, and many others.
Operating Divisions Full List:
– Administration for Children and Families (ACF)
—- Administration for Children, Youth and Families (ACYF)
– Administration on Aging (AoA)
– Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ)
– Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR)
– Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
– Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services
– Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
– Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA)
– Indian Health Service (IHS)
– National Institutes of Health (NIH)
—- National Cancer Institute (NCI)
– Office of the Inspector General (OIG)
– Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration
USA Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Staff Divisions.
The subdivisions of the Office of the Secretary provide direct support for the Secretary’s initiatives.
Staff Divisions Full List:
– Assistant Secretary for Administration (ASA)
– Assistant Secretary for Financial Resources (ASFR)
– Assistant Secretary for Legislation (ASL)
– Assistant Secretary for Public Affairs (ASPA)
– Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation (ASPE)
– Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR)
– Center for Faith-Based and Neighborhood Partnerships (CFBNP)
– Departmental Appeals Board (DAB)
– Intergovernmental Affairs and Regional Representatives (IGA)
– Office for Civil Rights (OCR)
– Office on Disability (OD)
– Office of the General Counsel (OGC)
– Office of Global Health Affairs (OGHA)
– Office of the Inspector General (OIG)
– Office of Medicare Hearings and Appeals (OMHA)
– National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC)
– Assistant Secretary for Health, Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health (ASH)

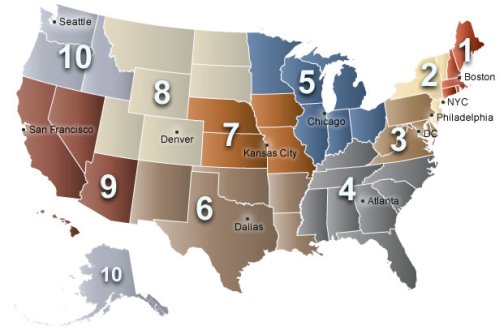
> USA Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Regional Offices.