Articles in Information

Simple Lifestyle Test May Assess Stroke Risk Adults who score higher on Life’s Simple 7 (LS7), a tool used to assess cardiovascular disease risk, may have a reduced risk of stroke, according to a large analysis. Even small improvements in lifestyle factors were associated with lower stroke risk. Stroke is the fourth leading cause of […]
Continue reading "Simple Lifestyle Test May Assess Stroke Risk" >>
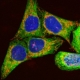
BACH2 Helps Orchestrate the Immune Response Scientists discovered how a gene called BACH2 may affect the development of multiple sclerosis, asthma, Crohn’s disease, celiac disease and other allergic and autoimmune diseases. Human T cells stained to reveal the DNA in their nuclei. Image by A. Walker, L. Sharp & J. Pryde./ All rights reserved by Wellcome Images. The […]
Continue reading "BACH2 Helps Orchestrate the Immune Response" >>

Vegetarian Diets Linked to Lower Mortality Adults who eat a more plant-based diet may be boosting their chance of living longer, according to a large analysis. Research has shown that the foods you eat influence your health. Eating certain foods, such as fruits and nuts, has been associated with reduced death rates, while other foods, […]
Continue reading "Vegetarian Diets Linked to Lower Mortality" >>

Brain Waves May Predict Autism Outcomes The brain activity of 2-year-olds with autism as they listen to words predicts thinking and language skills up to 4 years later. The finding hints that brain measurements may help to anticipate future abilities in children with autism and allow for early, personalized interventions. Autism spectrum disorders are a […]
Continue reading "Brain Waves May Predict Autism Outcomes" >>

Scientists Discover a Dedicated Pathway for Itch Researchers identified critical steps in the neural pathway for itchiness in mice, showing that it may be distinct from the circuits that allow us to feel heat and pain. The finding may point to new approaches for blocking the sometimes-debilitating itchiness of conditions such as psoriasis, shingles and […]
Continue reading "Scientists Discover a Dedicated Pathway for Itch" >>

Therapeutic Nanoparticles from Grapefruit Juice Researchers used nanoparticles derived from grapefruits to deliver targeted drugs to treat cancer in mice. The technique may prove to be a safe and inexpensive way to make customized therapies. Nanovectors derived from grapefruits can efficiently deliver a variety of therapeutic agents. Image courtesy of Zhang lab. Nanoparticles are emerging as […]
Continue reading "Therapeutic Nanoparticles from Grapefruit Juice" >>
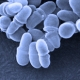
Fungal Findings A genomic survey of the fungi living on our skin provides a framework for understanding how these microbes contribute to skin health and disease. Malassezia fungi. Credit: Janice Haney Carr, CDC. Complex communities of microbes live on the surface of our bodies. These fungi, bacteria and viruses are collectively known as the skin microbiome. […]

Clues to Congenital Heart Disease A large-scale genomic analysis found that non-inherited mutations in hundreds of genes together account for about 1 in 10 cases of severe congenital heart defects. The findings bring us closer to understanding the most common type of birth defect. Congenital heart defects are problems with the heart’s structure that are […]
Continue reading "Clues to Congenital Heart DiseaseClues to Congenital Heart Disease" >>
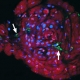
Infection Makes Mosquitoes Immune to Malaria Parasites Researchers established a bacterial infection in mosquitoes that helps fight the parasites that cause malaria. The infected insects could be a significant tool for malaria control. Wolbachia (green, indicated by white arrows) in an infected mosquito’s midgut. Image by the Xi lab, used courtesy of Science. Malaria is caused by a […]
Continue reading "Infection Makes Mosquitoes Immune to Malaria Parasites" >>
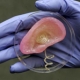
3-D Printing of Working Bionic Ears Researchers used 3-D printing of cartilage cells and nanomaterials to create functional ears that receive radio signals. The study demonstrates that it may one day be possible to create bionic tissues and organs. Scientists used 3-D printing to merge tissue and an antenna that receives radio signals. Photo by Frank Wojciechowski. […]