Egg-Producing Stem Cells Found in Women
Egg-Producing Stem Cells Found in Women
Researchers have isolated egg-producing stem cells from the ovaries of women and observed these cells giving rise to young egg cells, or oocytes. The finding may point the way toward improved treatments for female infertility.
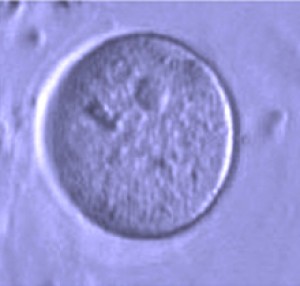
Egg-producing stem cells isolated from an adult human ovary can generate an oocyte (above) in culture. /Image by White et al., courtesy of Nature.
Researchers have long believed that women are born with a fixed number of oocytes that must last through their reproductive years. Common wisdom held that once oocytes were lost during ovulation or degeneration due to aging or disease, they couldn’t be replenished within adult ovaries.
In 2004, Dr. Jonathan Tilly of Massachusetts General Hospital and his colleagues reported the first evidence that mammals—specifically female mice—continue to form new oocytes into adulthood. That study, funded by NIH’s National Institute on Aging (NIA), was considered controversial by many. But follow-up research by Tilly and others supported the finding. Eventually, scientists pinpointed egg-producing stem cells within mouse ovaries.
To see if similar stem cells might also exist in women, Tilly led a team of scientists who tested and then validated a new method for plucking viable egg-producing stem cells from adult mice and human ovary tissue. Their research, supported in part by NIA, was described in the advance online edition of Nature Medicine on February 26, 2012.
The new technique is based on a marker protein called Ddx4, which was known to exist inside egg cells. The researchers showed that Ddx4 is also found on the surface of only a small population of ovarian cells, and that these rare cells have many properties of primitive precursors to oocytes. To isolate these rare cells, the scientists used fluorescence-tagged antibodies that latch onto cell-surface Ddx4. A fluorescence-based cell-sorting instrument then purified precursor cells taken from both mouse and human tissues.
The researchers showed that cells isolated from both mouse and human ovaries could grow in a culture dish and spontaneously generate cells that had many features of oocytes. To test how the mouse cells function within the body, the researchers inserted a gene for a green-glowing protein. They then injected the labeled cells into the ovaries of adult mice. After several months, the mouse ovaries included green-glowing egg cells, showing that the rare isolated cells could give rise to mature eggs. The green-labeled eggs were then successfully fertilized and produced multi-celled mouse embryos.
The researchers also used green fluorescent labeling to test the isolated human cells. The tagged cells were added to human ovarian tissue and then inserted into mice. Within 2 weeks, the human cells generated ovarian follicles containing green-glowing egg cells.
“The primary objective of the current study was to prove that oocyte-producing stem cells do in fact exist in the ovaries of women during reproductive life, which we feel this study demonstrates very clearly,” says Tilly. “The discovery of oocyte precursor cells in adult human ovaries, coupled with the fact that these cells share the same characteristic features of their mouse counterparts that produce fully functional eggs, opens the door for development of unprecedented technologies to overcome infertility in women and perhaps even delay the timing of ovarian failure.”
By Vicki Contie
###
* The above story is reprinted from materials provided by National Institutes of Health (NIH)
** The National Institutes of Health (NIH) , a part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, is the nation’s medical research agency—making important discoveries that improve health and save lives. The National Institutes of Health is made up of 27 different components called Institutes and Centers. Each has its own specific research agenda. All but three of these components receive their funding directly from Congress, and administrate their own budgets.