Malaria Vaccine Found Safe and Protective
Malaria Vaccine Found Safe and Protective
A candidate malaria vaccine is safe and protects against infection in adults, according to the results of an early-stage clinical trial.
Malaria is one of the most common infectious diseases in the world and an enormous public health problem. It kills hundreds of thousands of people each year, most of them young children in Sub-Saharan Africa. Currently, there is no effective malaria vaccine.
Malaria is caused by thePlasmodium parasite. Infection occurs when a person is bitten by a mosquito harboring 1 of 4 species of Plasmodium.
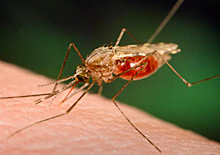
Anopheles funestus, a malaria-transmitting mosquito. Image by James Gathany, Dr. Frank Collins, University of Notre Dame, courtesy of CDC.
The PfSPZ Vaccine, developed by scientists at Sanaria Inc., is composed of a live but weakened version of Plasmodium falciparum, the most deadly malaria-causing parasite. The parasites are weakened by exposing them to radiation when they’re in the infective stage of development, called sporozoites. For many years, it wasn’t possible to purify these sporozoites from the mosquito. But scientists recently figured out how to isolate the weakened sporozoites so that they can be given in an injected vaccine.
A Phase I trial of the PfSPZ Vaccine took place at the NIH Clinical Center in Bethesda, Maryland. Led by Dr. Robert A. Seder at the Vaccine Research Center of NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), researchers enrolled 57 healthy adults, ages 18-45, with no previous malaria infection.
Forty participants received the PfSPZ Vaccine and 17 didn’t. The vaccine recipients were split into different dosage groups. Each group received 2-6 intravenous injections of increasing doses given 4 weeks apart. The results appeared online in Science on August 8, 2013.
After vaccination, participants were monitored closely for 7 days. No severe side effects or malaria infections developed. Those who received a higher total dosage of the vaccine had a greater immune system response.
To evaluate the protection provided by the PfSPZ Vaccine, the scientists collaborated with the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research and the Naval Medical Research Center. Participants were exposed to 5 bites by P. falciparum-infected mosquitoes 3 weeks after vaccination. They were then monitored for 7 days and tested for infection. Those who were diagnosed with malaria were treated with anti-malarial drugs and cured.
The researchers found that only 3 of the 15 who received the highest doses of the vaccine became infected from the mosquito bites. Of the 6 participants who received all 5 injections using this highest dose, none were infected. In contrast, 16 of 17 participants in the lower dosage group and 11 of 12 who received no vaccine became infected.
“Scientists and health care providers have made significant gains in characterizing, treating and preventing malaria; however, a vaccine has remained an elusive goal. We are encouraged by this important step forward,” says NIAID Director Dr. Anthony S. Fauci.
Several follow-up studies are now planned. They include exploring how long protection lasts and whether the vaccine could protect against other strains of P. falciparum. Among the future challenges is that this vaccine must be injected intravenously—a rare delivery route for vaccines—and stored in liquid nitrogen. This would require new infrastructure, especially in rural, developing regions where the vaccine would be most needed.
###
* The above story is reprinted from materials provided by National Institutes of Health (NIH)
** The National Institutes of Health (NIH) , a part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, is the nation’s medical research agency—making important discoveries that improve health and save lives. The National Institutes of Health is made up of 27 different components called Institutes and Centers. Each has its own specific research agenda. All but three of these components receive their funding directly from Congress, and administrate their own budgets.