3-D Printing of Working Bionic Ears
3-D Printing of Working Bionic Ears
Researchers used 3-D printing of cartilage cells and nanomaterials to create functional ears that receive radio signals. The study demonstrates that it may one day be possible to create bionic tissues and organs.
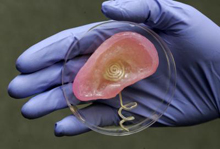
Scientists used 3-D printing to merge tissue and an antenna that receives radio signals. Photo by Frank Wojciechowski.
In tissue engineering, cells and other materials are used to improve or replace the body’s tissues, such as bone and cartilage. Currently, however, it’s difficult to create 3-D structures for use in the body, especially organs with complex geometries, such as ears.
To overcome this problem, a research team led by Dr. Michael McAlpine at Princeton University and Dr. David Gracias at Johns Hopkins University turned to additive manufacturing, or 3-D printing. In this process, a 3-D object is ‘printed’ by laying down successive layers of material in a pattern based on a digital model. The study, funded in part by an NIH Director’s New Innovator Award, appeared online on May 1, 2013, in Nano Letters.
The researchers used a computer-aided design (CAD) drawing of a human right ear as a blueprint for the printing. They used 3 components as the printer “inks”: cartilage cells in a hydrogel matrix, structural silicone, and silicone infused with silver nanoparticles. The ear was built layer by layer with an ordinary 3-D printer, with the silver-infused “ink” forming a coiled antenna.
Over a 10-week period in culture conditions, the hydrogel component of the printed ear was reabsorbed, and the cells developed an extracellular matrix, turning the ear opaque.
The researchers characterized the biochemical, mechanical and functional properties of the ear. They found that the “cyborg ear” could receive signals in a wide radio frequency range, with the inductive coil acting as a receiving antenna. The signal frequencies ranged from 1 MHz to 5 GHz.
To demonstrate the versatility of the approach, the researchers flipped the CAD design and created a complementary left ear. They exposed the ears to antenna signals of left and right stereophonic audio, collected the signals received by the ears, fed them into a digital oscilloscope, and played the resulting audio signals through loud speakers. The system produced high-quality audio, as demonstrated by a rendition of Beethoven’s Für Elise.
“In general, there are mechanical and thermal challenges with interfacing electronic materials with biological materials,” says McAlpine. “Our work suggests a new approach—to build and grow the biology up with the electronics synergistically and in a 3-D interwoven format.”
This proof-of-principle study shows that tissues and electronics can be combined to form hybrid, bionic organs. The team now plans to incorporate other materials to allow the ear to register acoustic sounds. 3-D printing could expand the opportunities for creating a new generation of implants and prostheses to restore—or even enhance—human capabilities.
By Carol Torgan, Ph.D.
###
* The above story is reprinted from materials provided by National Institutes of Health (NIH)
** The National Institutes of Health (NIH) , a part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, is the nation’s medical research agency—making important discoveries that improve health and save lives. The National Institutes of Health is made up of 27 different components called Institutes and Centers. Each has its own specific research agenda. All but three of these components receive their funding directly from Congress, and administrate their own budgets.